Oct 15, 2023Anatomical Position The testes are located within the scrotum, with the epididymis situated on the posterolateral aspect of each testicle. Commonly, the left testicle lies lower than the right. They are suspended from the abdomen by the spermatic cord – collection of vessels, nerves and ducts that supply the testes.
Testis and Epididymis
Jul 27, 2022Figure 23.2.1 23.2. 1: Male Reproductive System. The structures of the male reproductive system include the testes, the epididymides, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. Sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord.
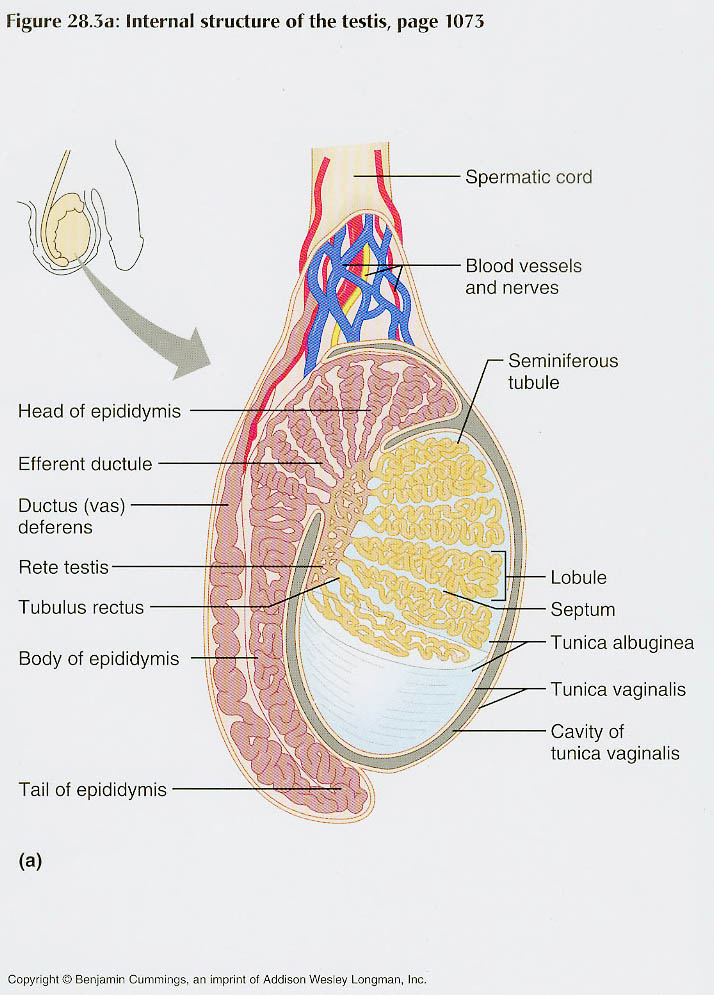
Source Image: galeps.org
Download Image
Figure 27.2 Testicular Reproductive System The structures of the testicular reproductive system include the testes, the epididymides, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. Sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Best Epididymis Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock The structure of the penis and its location relative to other reproductive organs are shown in Figure 22.3.4 22.3. 4. The part of the penis that is located inside the body and out of sight is called the root of the penis. The shaft of the penis is the part of the penis that is outside the body. The enlarged, bulbous end of the shaft is called

Source Image: in.pinterest.com
Download Image
Art-Labeling Activity: Internal Structures Of The Testis And Epididymis
The structure of the penis and its location relative to other reproductive organs are shown in Figure 22.3.4 22.3. 4. The part of the penis that is located inside the body and out of sight is called the root of the penis. The shaft of the penis is the part of the penis that is outside the body. The enlarged, bulbous end of the shaft is called West Hills College Lemoore. Table of contents. Laboratory Activities and Assignment. Part 1: Review of the Reproductive Systems. Part 2: Histology of the Reproductive Systems. Ovary. Testis. Part 3: Reproductive Systems Laboratory Activities. Labeling Male Reproductive Anatomical Model (s)
Sagittal Section Of Testis | Medical school essentials, Biology diagrams, Anatomy
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Overview, Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Meiosis I, Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Meiosis II and more. … Art-Labeling Activity: Internal organs of the male reproductive system midsagittal section. Art-Labeling: Internal structures of the testis and epididymis ANSWERED] Art labeling Activity The Epididymis … – Anatomy and Physiology – Kunduz
![ANSWERED] Art labeling Activity The Epididymis ... - Anatomy and Physiology - Kunduz](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20230327212821612172-4484176.jpg)
Source Image: kunduz.com
Download Image
Testis and Epididymis – ScienceDirect Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Overview, Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Meiosis I, Bioflix Activity: Meiosis- Meiosis II and more. … Art-Labeling Activity: Internal organs of the male reproductive system midsagittal section. Art-Labeling: Internal structures of the testis and epididymis

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Testis and Epididymis Oct 15, 2023Anatomical Position The testes are located within the scrotum, with the epididymis situated on the posterolateral aspect of each testicle. Commonly, the left testicle lies lower than the right. They are suspended from the abdomen by the spermatic cord – collection of vessels, nerves and ducts that supply the testes.

Source Image: netterimages.com
Download Image
Best Epididymis Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Figure 27.2 Testicular Reproductive System The structures of the testicular reproductive system include the testes, the epididymides, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. Sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Testis tissue hi-res stock photography and images – Page 2 – Alamy Nov 3, 2023The tunica vaginalis is the peritoneal sac that partially encloses the testes. It is derived from the embryonic vaginal process.This process is the outpouching of the parietal peritoneum, which follows the testes during descent and then encloses them.It has parietal and visceral layers. The visceral (internal) layer covers the testis, the head of epididymis, and the inferior part of ductus

Source Image: alamy.com
Download Image
Servier – Drawing Testis and epididymis – no labels | AnatomyTOOL The structure of the penis and its location relative to other reproductive organs are shown in Figure 22.3.4 22.3. 4. The part of the penis that is located inside the body and out of sight is called the root of the penis. The shaft of the penis is the part of the penis that is outside the body. The enlarged, bulbous end of the shaft is called
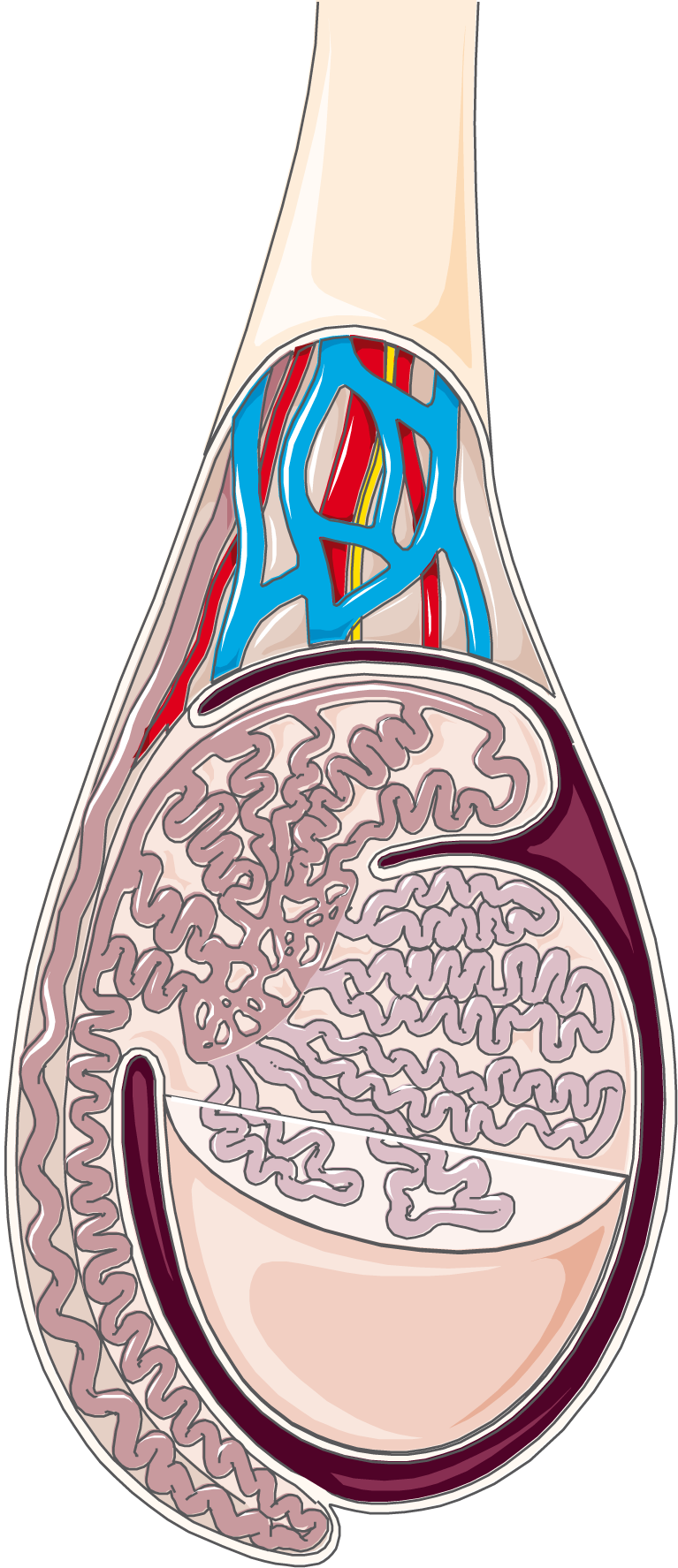
Source Image: anatomytool.org
Download Image
PPT – Lab # 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:2367669 West Hills College Lemoore. Table of contents. Laboratory Activities and Assignment. Part 1: Review of the Reproductive Systems. Part 2: Histology of the Reproductive Systems. Ovary. Testis. Part 3: Reproductive Systems Laboratory Activities. Labeling Male Reproductive Anatomical Model (s)

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
Testis and Epididymis – ScienceDirect
PPT – Lab # 10 PowerPoint Presentation, free download – ID:2367669 Jul 27, 2022Figure 23.2.1 23.2. 1: Male Reproductive System. The structures of the male reproductive system include the testes, the epididymides, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. Sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord.
Best Epididymis Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Servier – Drawing Testis and epididymis – no labels | AnatomyTOOL Nov 3, 2023The tunica vaginalis is the peritoneal sac that partially encloses the testes. It is derived from the embryonic vaginal process.This process is the outpouching of the parietal peritoneum, which follows the testes during descent and then encloses them.It has parietal and visceral layers. The visceral (internal) layer covers the testis, the head of epididymis, and the inferior part of ductus